Fact Sheet
How Does the Brain Develop, Grades 9-12
Who this is for:

We cannot see them with our eyes, but our bodies are made up of trillions of cells. Based on the incredible number and diversity of cells we have as adults, it’s hard to believe we started out as one tiny solemn cell.
How did something so complex originate from only one cell?
In a fascinatingly complex series of events during early pregnancy, one fertilized cell divides into a small mass of identical cells known as stem cells. Stem cells are special in that they can turn into almost any type of cell in the body; hair, skin, bone, nerve cells. As these cells continue to multiply, specific genes within the cells are turned on and begin giving instructions via chemical signals to aid in development
What makes the neural tube?
As cells divide, they separate into three germ layers known as the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm.
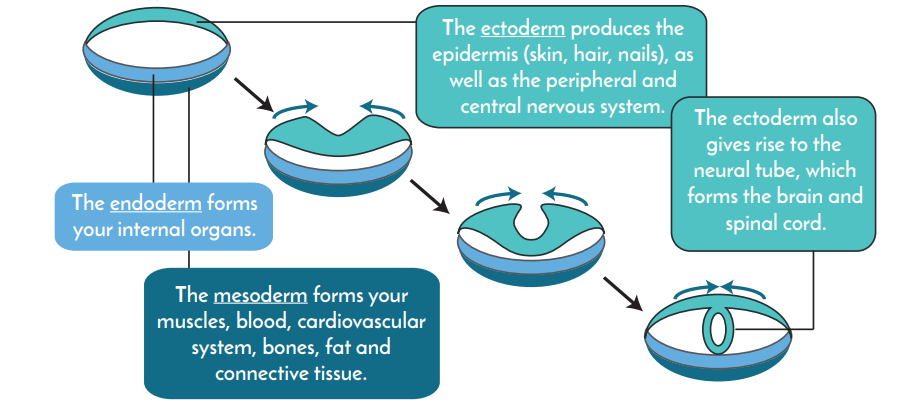

At approximately the third week of gestation, or development, the neural tube begins to form within the ectoderm layer. The neural tube is the first step of brain development. Special stem cells, known as neural progenitor cells, are created within the neural tube. Neural progenitor cells continuously divide, forming two new progenitor cells with each division.
About six weeks into gestation, neural progenitors begin to divide in a new way: each division creates one progenitor cell, and one neuron. The back of the neural tube will create the neurons of the spinal cord, while the front part of the neural tube produces neurons that will eventually be part of the brain. Unlike neural progenitor cells, neurons can no longer divide.
Where do the neurons go?
As new neurons are created, they migrate from the neural tube to new destinations to form parts of the brain and spinal cord. Complex chemical signals determine where new neurons will migrate, and which brain structures they ultimately contribute to. These chemical signals provide directions, much like a map, to each neuron. Once neurons reach the end of their journey, it’s time for them to set up shop. They grow special branches, known as dendrites and axons, that connect with other neurons.
Neurons also mature with the help of non-neuron cells called glia. Glial cells not only provide chemical signals like breadcrumbs, but at times, can also provide physical architecture to assist with migration. For example, glial cells known as Bergmann glia act as a branch on which two cerebellar neurons, Purkinje and granule cells, will climb through the brain to their ultimate destination of the cerebellum.
What changes after birth?
The developing brain engages in an intricate dance with its outside environment and is a sponge for information. During early development, 700 to 1,000 new neural connections are formed every second.
These early connections are the fundamental groundwork and precursors for more sophisticated connections later on. Although it is very important for new neurons to form long-lasting connections, it is equally important to trim away unnecessary connections. This process, known as synaptic pruning, allows only very important and useful connections to remain, while unused links between neurons are removed. Synaptic pruning occurs a great deal in early childhood, but also occurs during adolescence and adulthood.
Not only are connections between neurons regulated, but the actual number of neurons is also regulated by something known as programmed cell death, or apoptosis. Embryonic development gives rise to an overproduction of neurons. Although still not completely understood, apoptosis during this time occurs in response to both environmental and genetic factors.
New neurons make up only a small percentage of the total number of neurons in the adult brain. New connections between neurons, on the other hand, are constantly being formed, removed, and replaced. New connections are made when you learn skills and make memories. Connections can be lost when you fail to use or strengthen them. New research suggests that certain parts of your brain, especially areas involved in planning and working memory—also known as short-term memory—continue to develop and mature their connections well into your twenties.